The First Book of Moses: Called Genesis
From creation and the fall of humanity through the primeval history of judgment and scattering, to God's covenant promises to the patriarchs
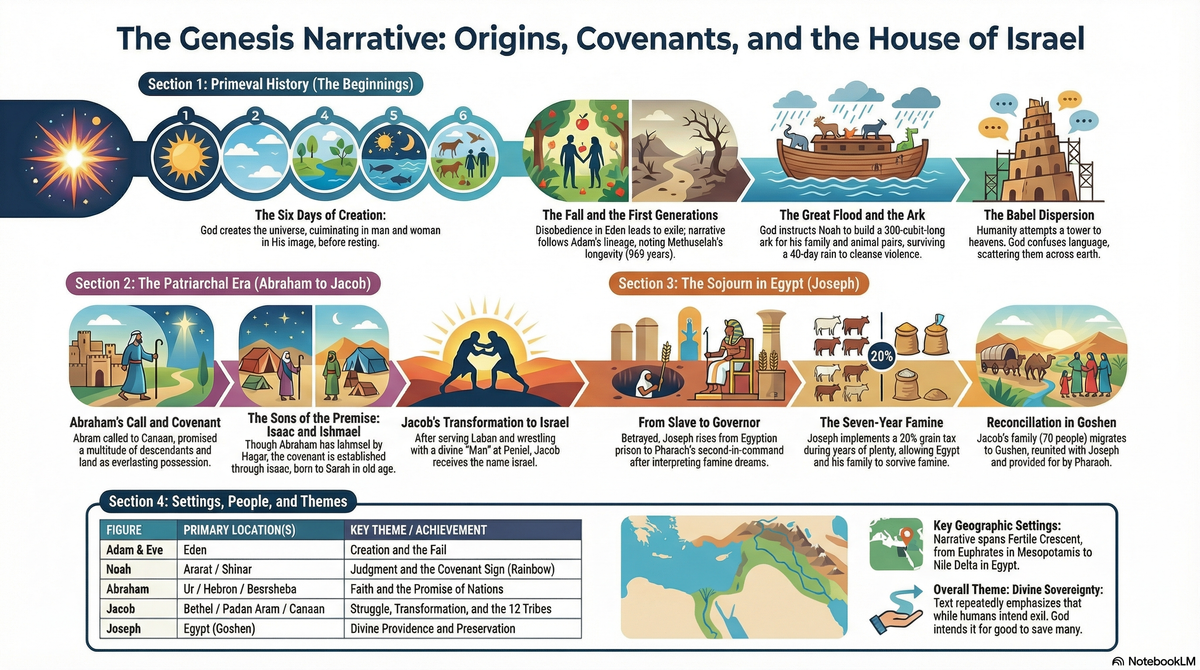
Summary
Genesis, the opening book of the Bible, lays the foundation for the entire scriptural narrative. It answers fundamental questions about origins: where the world came from, why humanity exists, the source of sin and suffering, and how God begins to restore what was broken through chosen people and covenant promises. Traditionally attributed to Moses, it covers events from creation to the death of Joseph in Egypt (spanning perhaps thousands of years in primeval history and several centuries in the patriarchal era). The book divides into two major sections: chapters 1–11 (universal history of humanity) and chapters 12–50 (focused patriarchal history leading toward the nation of Israel).
Overall Theme:
The overarching theme of Genesis is God's sovereign plan of creation, judgment, and redemption initiated through covenant. From the perfect ordered creation in Genesis 1–2 to the fall in chapter 3, humanity's repeated rebellion leads to divine judgment (flood, Babel), yet God never abandons His creatures. Instead, He chooses one man—Abraham—and makes unbreakable promises: to make him a great nation, bless him, give his descendants the land of Canaan, and through his seed bless all families of the earth (12:1–3; repeated and expanded to Isaac and Jacob). This covenant theme drives the narrative, showing God's faithfulness amid human failure, family conflict, deception, and hardship. Genesis portrays God as Creator, Judge, and Promise-Keeper who works providentially through flawed families to bring blessing to the world, foreshadowing the gospel (the ultimate "seed" of Abraham in Christ – Galatians 3:16).
Location Settings
Primeval History (chs. 1–11):
- Eden — The original paradise garden planted by God in the east (2:8).
- The ancient Near East broadly — Cain's land of Nod (east of Eden), the pre-flood world, Mount Ararat (where the ark rested, 8:4), Shinar/Babel (Mesopotamia/Iraq region, 11:2).
These chapters have a universal scope with minimal specific geography after Eden.
Patriarchal History (chs. 12–50):
- Canaan (Promised Land) — Central setting: from Shechem, Bethel, Hebron (Mamre), Beersheba, Gerar, to the Negev. Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob live as semi-nomadic herders here.
- Egypt — Major location in the later chapters: Abraham's brief sojourn (12), but especially Joseph's rise from slave to ruler, the family's relocation during famine (chs. 37–50), ending with Jacob's death and Joseph's burial instructions.
- Haran (Paddan Aram) — In northern Mesopotamia, home of Laban; where Jacob flees and marries Leah and Rachel.
- Sodom and Gomorrah — Cities of the plain destroyed by fire (ch. 19).
The focus narrows from the whole earth to Canaan and Egypt as the stage for God's covenant people.
People Involved
God (Yahweh / Elohim / LORD God)
The eternal Creator, sovereign over all, who speaks creation into being, judges sin, yet shows grace through covenants and providence.
Adam and Eve:
First humans, created in God's image; their disobedience introduces sin and death.
Cain and Abel:
First sons of Adam/Eve; Cain murders Abel out of jealousy.
Noah:
Righteous man who builds the ark; survives the flood with his family; receives the rainbow covenant.
Abraham (Abram):
Called from Ur/Haran at age 75; father of faith, recipient of the Abrahamic covenant; tested in faith (e.g., offering Isaac).
Sarah (Sarai):
Abraham's wife; barren until old age; mother of Isaac; laughs at God's promise but sees fulfillment.
Isaac:
Miracle son of Abraham/Sarah; quieter figure; marries Rebekah; father of Esau and Jacob.
Rebekah:
Wife of Isaac; helps Jacob receive the blessing; mother of Esau and Jacob.
Jacob (later Israel):
Deceiver who wrestles with God; receives the covenant; fathers the twelve tribes through Leah, Rachel, Bilhah, Zilpah.
Esau:
Jacob's twin brother; sells birthright; fathers Edomites.
Joseph:
Favored son of Jacob/Rachel; sold into slavery by brothers; rises to power in Egypt; saves family during famine; forgives brothers.
Supporting figures:
Lot (Abraham's nephew), Hagar and Ishmael (Abraham's son by Hagar), Laban (Rebekah's brother), Pharaohs of Egypt, twelve sons of Jacob (Reuben, Simeon, Levi, Judah, etc.).
Detailed Chapter Summary
Chapters 1–2 – Creation and paradise
God creates the heavens and earth in six days, culminating in humanity (male and female) in His image. He rests on the seventh day. Detailed account of man's formation from dust, placement in Eden, naming animals, and creation of woman from man's rib. Marriage instituted; all is "very good."
Chapters 3–4 – The fall and first murder
The serpent deceives Eve; both eat forbidden fruit; sin enters, bringing shame, curse, expulsion from Eden. Cain kills Abel; God marks Cain for protection.
Chapters 5–9 – Genealogies, corruption, and the flood
Line from Adam to Noah; increasing wickedness prompts God to limit human life to 120 years. Noah, blameless, builds ark; flood destroys all except Noah's family and animals. Post-flood covenant with rainbow; Noah's drunkenness and Ham's sin.
Chapters 10–11 – Table of nations and Babel
Descendants of Noah's sons (Shem, Ham, Japheth) populate earth. Humanity unites at Babel to build tower; God confuses languages and scatters them.
Chapters 12–25 – Abraham's call and life
God calls Abram to leave Haran for Canaan, promising land, nation, blessing. Abram journeys; sojourns in Egypt (lies about Sarai). Separates from Lot; Lot rescued from kings. Covenant renewed (ch. 15); Hagar bears Ishmael. Name change to Abraham/Sarah; circumcision covenant (ch. 17). Sodom/Gomorrah destroyed; Lot's daughters. Isaac born; Ishmael sent away. Abraham tested with Isaac's near-sacrifice (ch. 22). Sarah dies; Isaac marries Rebekah.
Chapters 25–36 – Isaac and Jacob
Birth of Esau and Jacob; Esau sells birthright. Isaac in Gerar (lies about Rebekah). Jacob deceives Isaac for blessing; flees to Laban. Jacob's dream at Bethel; marries Leah/Rachel; fathers children; prospers despite Laban's deceit; wrestles God; renamed Israel. Returns; reconciles with Esau. Dinah incident; Jacob at Bethel again.
Chapters 37–50 – Joseph and the preservation of the family
Joseph's dreams anger brothers; sold into Egypt; falsely imprisoned; interprets dreams; rises to second-in-command. Famine brings brothers; Joseph reveals himself, forgives, brings family to Egypt. Jacob blesses sons (Judah's line highlighted); dies. Joseph reassures brothers; dies, requests bones to Canaan.
Closing Prayer
Eternal God, Creator of heaven and earth, who spoke light into darkness and formed humanity from dust, we thank You for the book of beginnings that reveals Your sovereign hand from Eden to Egypt. In the face of sin's curse and humanity's rebellion, You preserved a remnant through Noah, called Abraham in grace, and worked through flawed families to advance Your promise of blessing for all nations. Grant us faith like Abraham's, forgiveness like Joseph's, and trust in Your providential plan until the Seed of the woman crushes the serpent's head and all Your promises are fulfilled in Christ. To You be glory forever. Amen.
Try Pastor Mugs App
Your KJV Pocket Companion. Faithful insights, verse clarity, guided prayers—ready whenever you open the Word.
Start Free, no strings ->